15/5/15 simple greenhouse for kids – how to build it Simply take two clear cups, turn one upside down, add soil and seeds Secure with tape, and punch three small holes in the top Tada!The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it Greenhouse effect is a concern for students due to the fact that they should know about the pros and cons of certain activities that involve heat radiation beyond the atmospheric level Greenhouse gases have reportedly elevated the mortality rate over the past many years

2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram
Greenhouse effect model simple
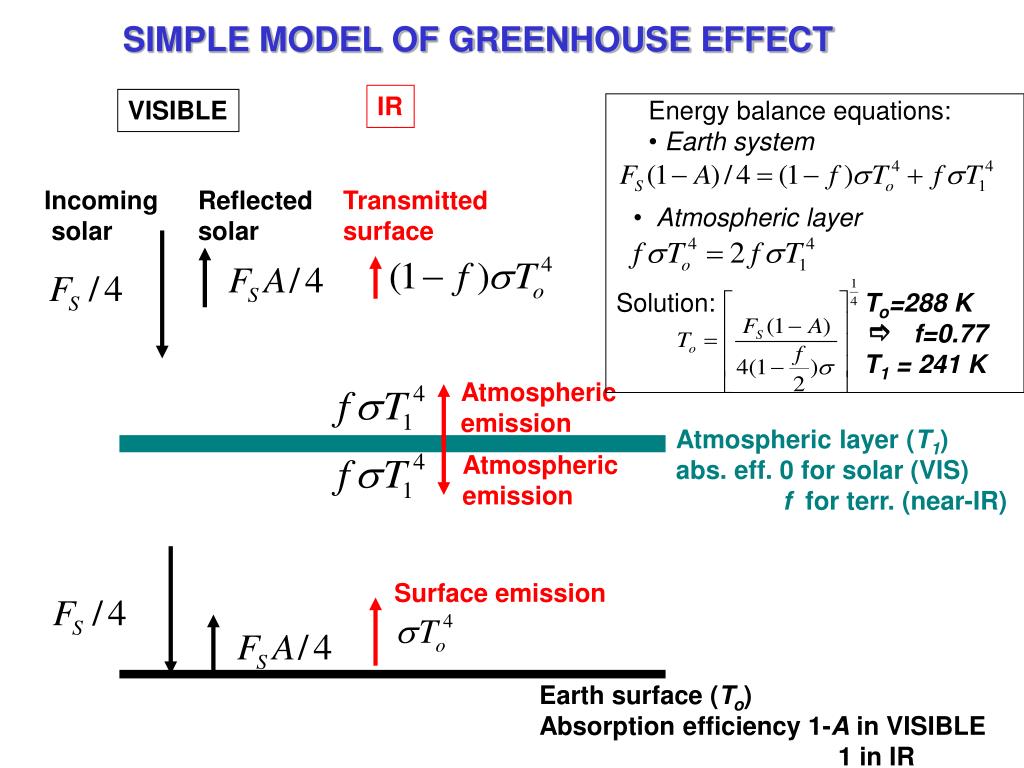
Greenhouse effect model simple-We can increase the complexity of the zerodimensional model by incorporating the atmospheric greenhouse effect in a slightly more realistic manner than is embodied by the ad hoc gray body model explored in the previous lecture We now include an explicit atmospheric layer in the model, which has the ability to absorb and emit infrared radiation1) The Greenhouse E ect Radiative equilibrium model for a single layer atmosphere Simple models are often applied in climate sciences as a tool for illustrating fundamental physical processes These models should not be considered as compact description of the complex real world Rather they help us




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Greenhouse effect model science exhibition project diy school fair project#greenhouseeffectmodel #scienceexhibition #howtofundaExplanation Video httpThis is a simple model of the greenhouse effect that is analogous to the atmosphere's ability to trap heat When the Sun's energy reaches Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back into space by the denser layers of the atmosphere, particulate matter, cloud tops,Activity 11 Understanding the Greenhouse Effect Grades 7 – 9 Description In Part 1 Modeling the Greenhouse Effect, students will do a lab that demonstrates the greenhouse effect, and will discuss the results of the lab In Part 2 The Earth's Energy Balance, students will color in
These simple models may also consider the effects of greenhouse gases At the other end of the spectrum are fully coupled, threedimensional, global climate models These are complex models that solve for radiative balance;An idealised model of the natural greenhouse effect See text for explanation (continued) Frequently Asked Questions water vapour is much greater The same is true for the cold, dry upper atmosphere where a small increase in water vapour has aThis lab exercises your understanding of "layer models" of the greenhouse effect These are also called "isothermal slab models," or "glass atmosphere models" They have serious shortcomings in their neglect of the way thermodynamics and convection alters the vertical temperature structure of real atmospheres, but they are still useful in understanding the basic way the greenhouse effect
Simple Mathematical Models of the Greenhouse Effect, and Global Warming Mathematical Models • Because models are simple, it is easier to see how the real system approximately works • More equations can be added to a model untilGreenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Students consider what happens when there is more carbon than usual in the atmosphere They then model the greenhouse effect of Earth's atmosphere through a handson experiment Finally, students deepen their understanding of the greenhouse effect by watching a short video and undertaking a reading andDon't knock it 'til you've tried itsometimes it's the simplest of things that are definitely the most fun!




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




In This Video We Make A Simple And Easy Greenhouse Effect Model Displaying The Process Science Exhibition Projects Greenhouse Effect Science Projects For Kids
Your own little redneck greenhouse!The balance of energy flow, as incoming sunlight and outgoing infrared, allow us to create our first simple climate model, including a simple greenhouse effect There are two extended exercises in Part II of this class, one an analytical (algebraic) model of the equilibrium temperature of a planet, the other a numerical model of how that temperature might evolve through time The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides



Environment For Kids Global Warming




What Is Climate Change Acciona Business As Unusual
This simple model always predicts a decreasing temperature away from the surface, and all levels increase in temperature as "greenhouse gases are added" Neither of these effects are fully realistic in the real atmosphere temperatures increase above the tropopause, and temperatures in that layer are predicted (and observed) to decrease as GHG's are addedGreenhouse effect PowerPoint presentation, prepainted greenhouse effect artwork MSLS23 Develop a model to describe the cycling of matter and flow of energy among Examples of simple molecules are water, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methaneFirst Climate Model The balance of energy flow, as incoming sunlight and outgoing infrared, allow us to create our first simple climate model, including a simple greenhouse effect There are two extended exercises in Part II of this class, one an analytical (algebraic) model of the equilibrium temperature of a planet, the other a numerical



7 Elementary Greenhouse Models The Climate Laboratory




Global Surface Temperature Trend 15 17 Nasagistemp 18
1/1/15 Joseph Postma published an article criticizing a very simple model that nonetheless produces useful results He made several very simple errors along the way, none of which are very technical in nature In no way does Postma undermine the existence or necessity of the greenhouse effect Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding onto some of Earth's heat energy so that it doesn't all escape into space This heat trapping is known as the greenhouse effect Just as too little greenhouse gas makes Earth too cold, too much greenhouse gas makes Earth too warm Over the last century, humans have burned coal, oil, andThe most important greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide(CO 2), and




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



1
However, scientists can make estimates about future population growth, greenhouse gas emissions, and other factors that affect climate They can enter those estimates into computer models to find out the most likely effects of global warming The IPCC predicts that greenhouse gas emissions will continue to increase over the next few decadesThe gray body model is a very crude way of accounting for the greenhouse effect in the context of a simple zerodimensional model In Lesson 5, we will build our way up to more realistic representations of the atmospheric greenhouse effectFor laws of motion governing the atmosphere , ocean , and ice ;




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Simple Climate



Simple Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse effect definition, an atmospheric heating phenomenon, caused by shortwave solar radiation being readily transmitted inward through the earth's atmosphere but longerwavelength heat radiation less readily transmitted outward, owing to its absorption by atmospheric carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and other gases;The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to existThe Very Simple Climate Model is, as the name implies, very simple In this model, average global temperature is determined entirely by the atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration via greenhouse warming of the atmosphere and uptake of carbon dioxide by the ocean and biosphere, which are kept constant through time




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Global Warming For Kids A Simple Explanation Of Climate Change
23/1/19 What is global warming, explained The planet is heating up—and fast Glaciers are melting, sea levels are rising, cloud forests are dying, and Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear French mathematician JosephStudents observe teacherled demonstrations, and build and evaluate simple models to understand the greenhouse effect, the role of increased greenhouse gas concentration in global warming, and the implications of global warming for engineers, themselves and the Earth In an associated literacy activ




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram



Green House 16 Greenhouse Effect Project Ppt
Greenhouse Atmosphere Let's Heat Things Up!5/2/ In this post, we will explore a simple model that illustrates the key features and science behind the greenhouse effect According to Wikipedia, a greenhouse gas is "a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range" These gases are transparent to the radiation from the sun which is generally of aThus, the rising level of carbon dioxide is viewed



Mr G S Environmental Systems 6 1 1 The Natural Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Observe the Greenhouse Effect in a Jar This experiment gets kids exploring how a greenhouse works, and in turn how greenhouse gases affect the Earth's atmosphere Your child will strengthen observation and recording skills, work with a control, and draw conclusions And bonus this is a great outdoor activity! The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some ofMathematical Models • Models are necessarily oversimplified and cannot accurately and comprehensively represent all details of a complex system • Because models are simple, it is easier to see how the real system approximately works • More equations can be added to a model until it becomes too difficult to understand or simulate on a computer



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Simple Experiment Showing Greenhouse Effect Stock Image E100 0145 Science Photo Library
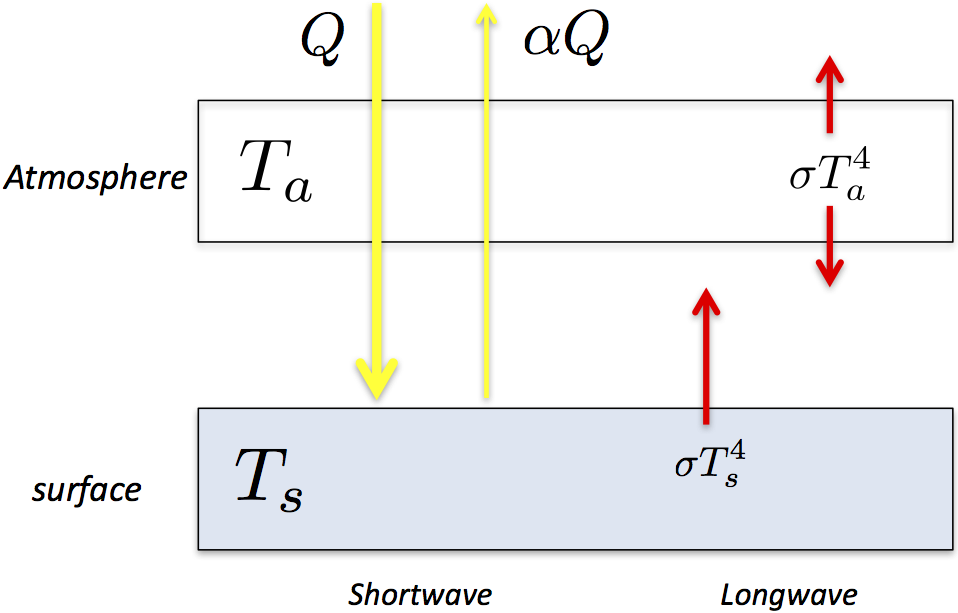
And for exchanges of energy and momentum within and between the different components of theYou just showed a small greenhouse effect This simple experiment serves as an introduction to the greenhouse effect Model the Coriolis Effect on a hurricane's direction 3rd grade Science project The Mozart Effect Science project The Mozart Effect ThisSimple model of greenhouse effect #1 single layer gray energy balance model Let's include the atmosphere assuming that it emits (absorbs) as a gray body Assume that the atmosphere does not absorb solar radiation all is absorbed at the surface TOA balance 0 (1 ) 4 4 4 s a r T F 2410




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
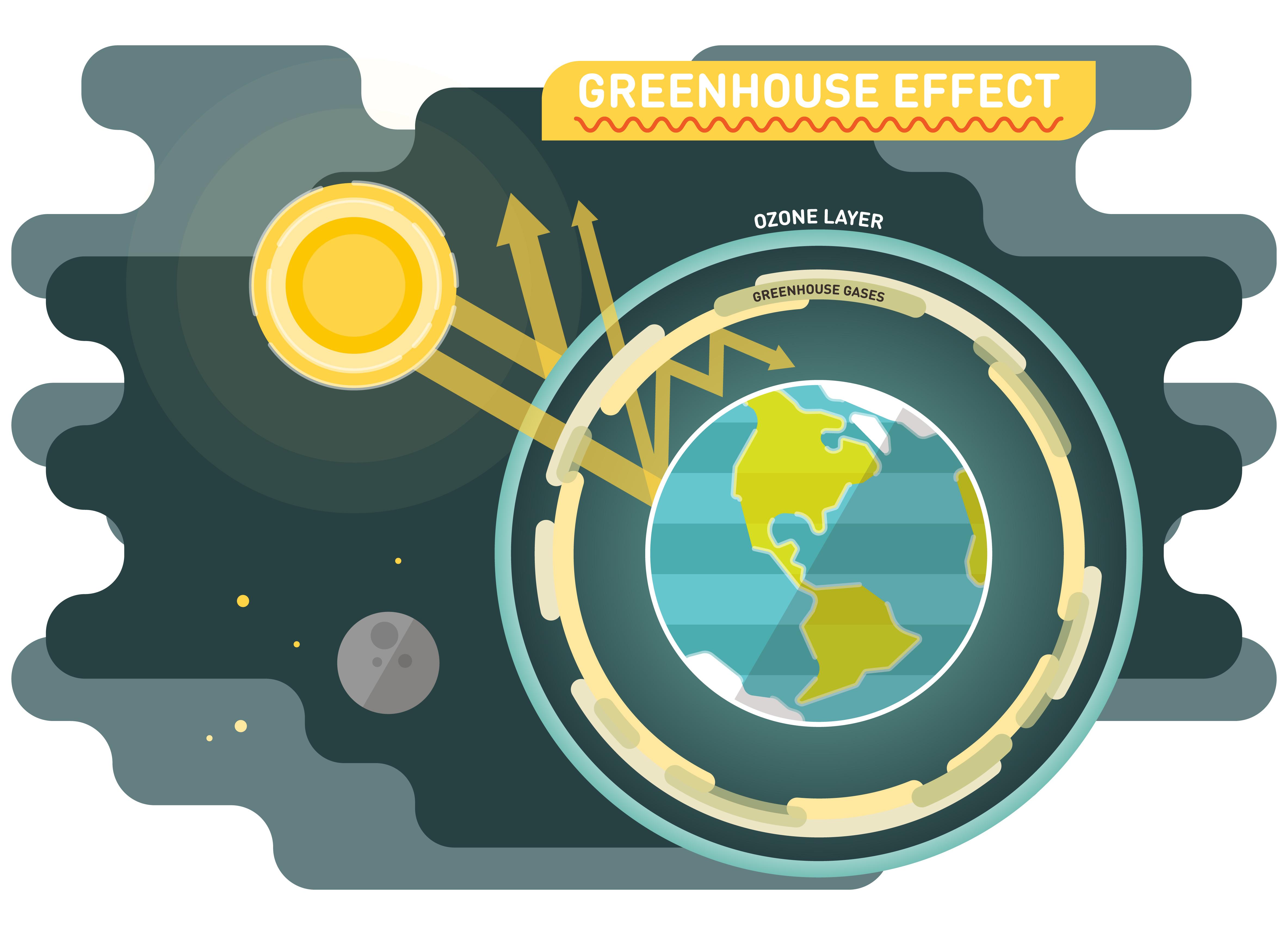



Why The Greenhouse Effect Is Important How It Affects The Climate
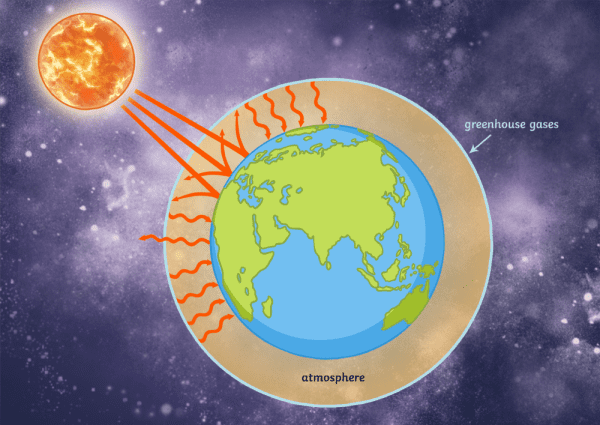
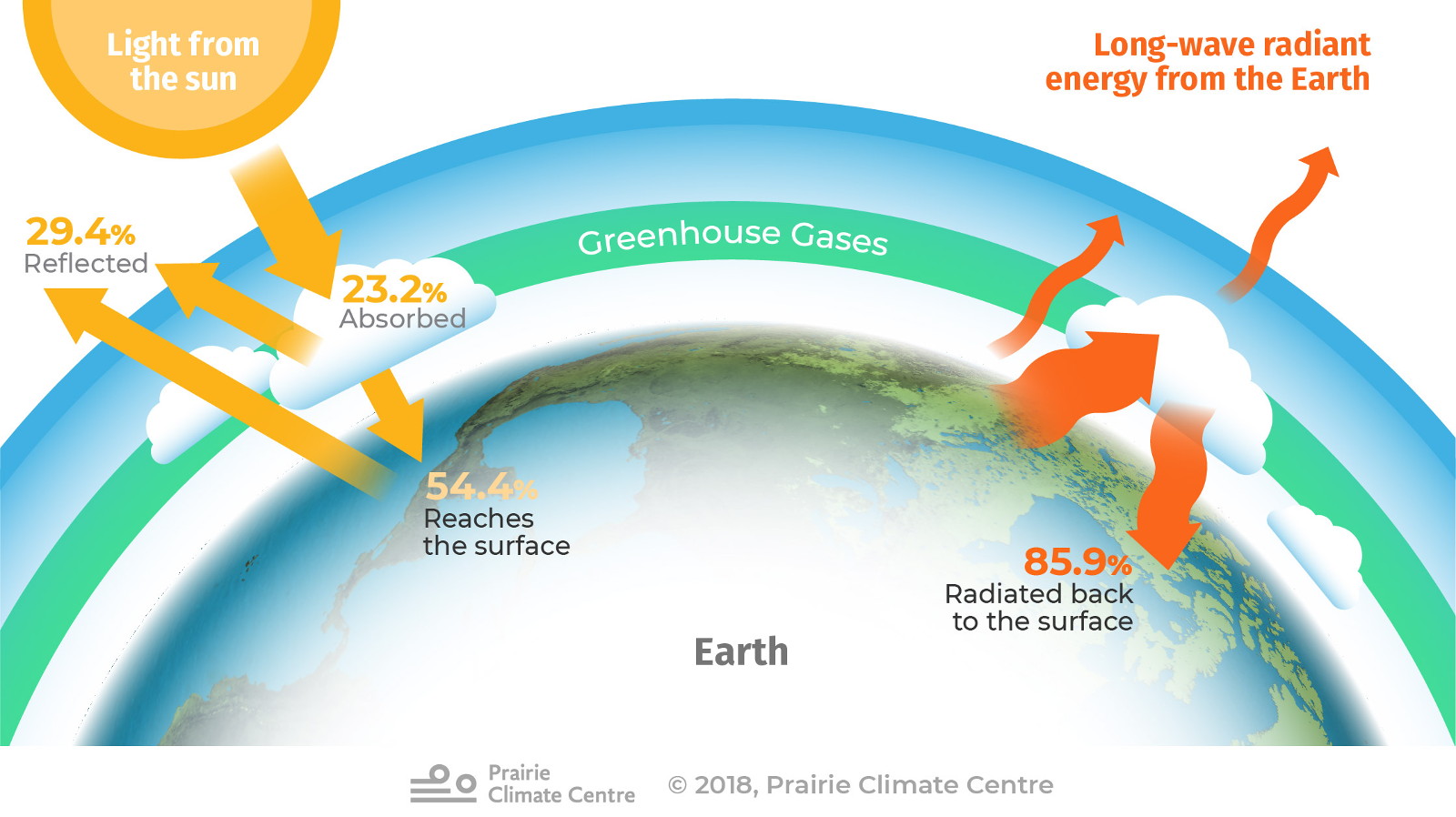
22/5/19 Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect Perhaps the most impressive of cloud formations, cumulonimbus (from the Latin for "pile" and "rain cloud") clouds form due to vigorous convection (rising and overturning) of warm, moist and unstable air greenhouse effect The warming of the Earth's surface due to greenhouse gases greenhouse gases Gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect (mainly carbon dioxide, methane and water) model (noun) A representation of something for imitation, comparison or analysis, sometimes on a different scale The greenhouse effect is where molecules in the atmosphere absorb infrared radiation and radiate it in all directions This means that that about one half is radiated downward toward Earth's surface The term cloud blanket effect is used to denote phenomenon in which the underside of a cloud reflects back down the infrared radiation that the Earth's surface is radiating
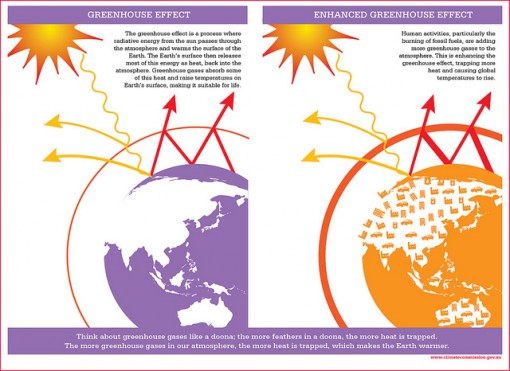



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering
The greenhouse effect occurs when certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere (the air around the Earth) trap infrared radiationThis makes the planet become warmer, similar to the way it makes a greenhouse become warmer The greenhouse effect is caused by greenhouse gases;Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box This teaching box provides resources related to the greenhouse effect It will help you teach how the greenhouse effect works, and how it prevents Earth from becoming a frozen ball of ice, and why there is too much of it happening today Teaching Boxes are collections of classroomready and standardsalignedHuman action is causing an increase in global temperature For that reason, the greenhouse effect, far from being our great ally as was the case in the past, is now a risk to our survival The flooding of coastal cities, the desertification of fertile areas, the melting of glacial masses and the proliferation of devastating hurricanes are just some of the main consequences
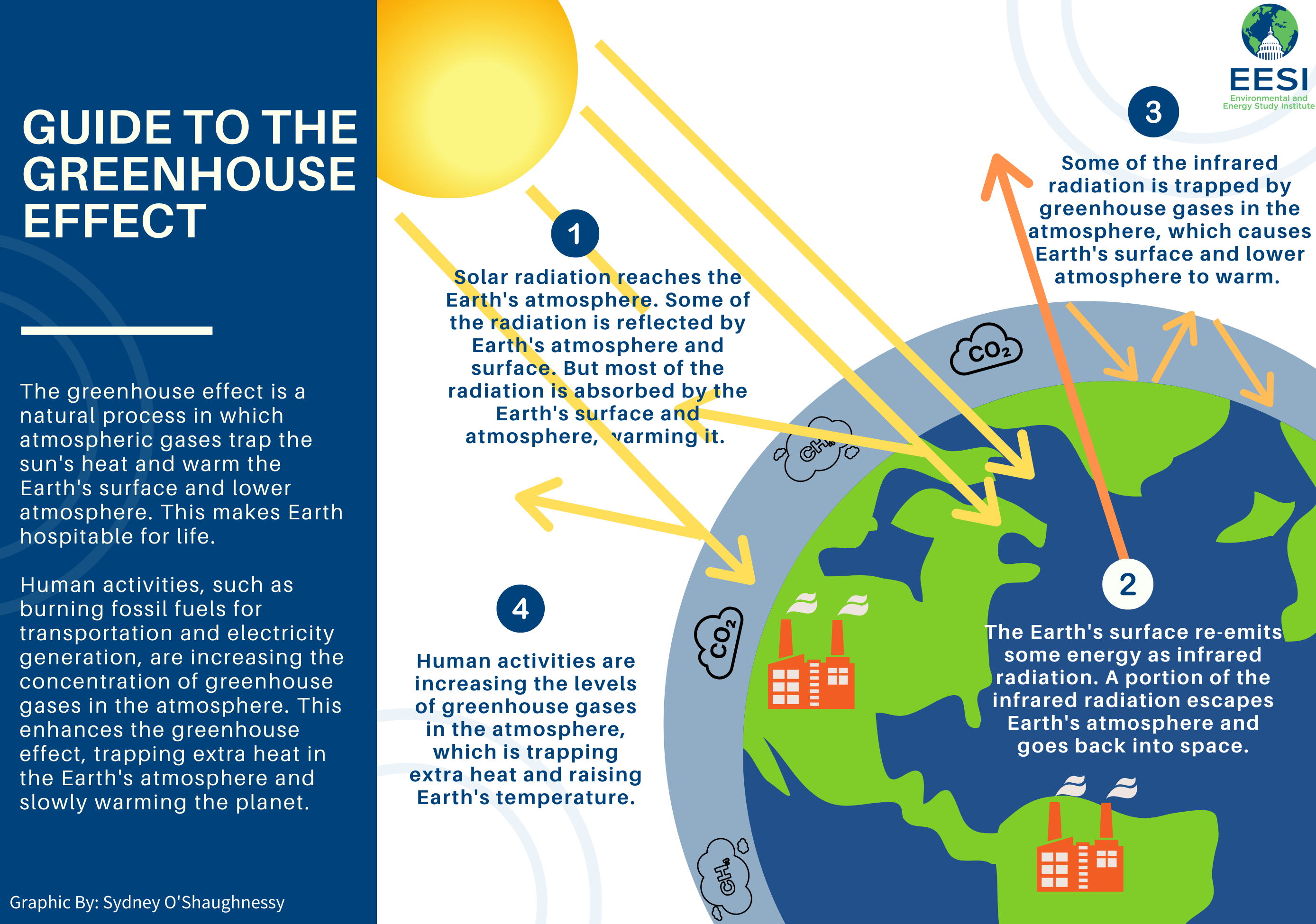



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi
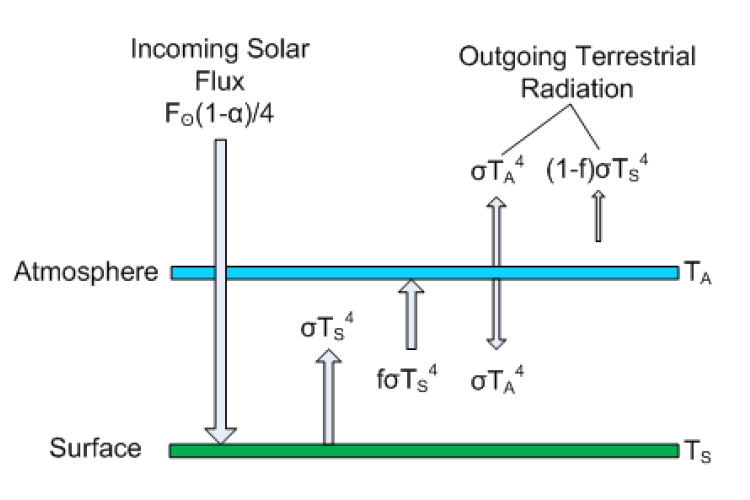



Joseph Postma And The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Simple Atmospheric Models Part One The Science Of Doom




Geo Expro Recent Advances In Climate Change Research Part Iii A Simple Greenhouse Model



The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
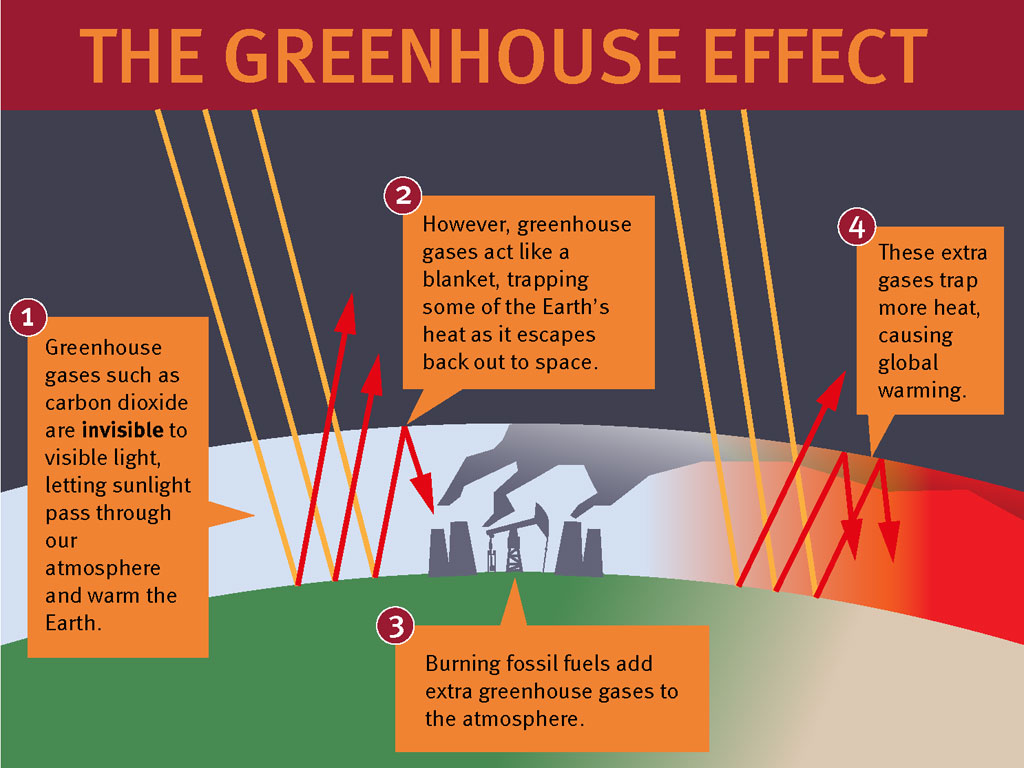



Greenhouse Effect




Specific Interpretations Greenhouse Gases 101 Sustainability



File Greenhouse Effect Svg Wikimedia Commons




Objectives 1 To Understand The Greenhouse Effect 2 To Use Simple Experimentation Techniques Including Observing And Recording Data Use Of A Control Ppt Download




A Simple Mathematical Model Of The Greenhouse Effect Coriolis Force



What Would You Say To Someone Who Says The Greenhouse Effect Can T Be Real Because The Second Law Of Thermodynamics Says Something Cooler Can T Raise The Temperature Of Something Warmer Quora




Simple Model Of The Greenhouse Effect Includes Atmosphere Layer Atmosphere Layer Passes All Solar Radiation Atmosphere Layer Absorbs All Ir From Earth Ppt Download
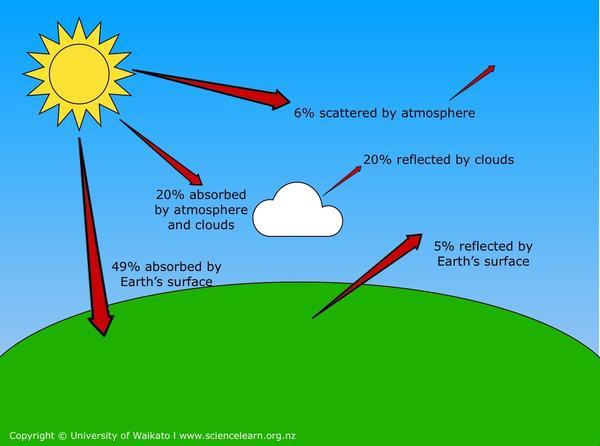



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub




6 2 The Greenhouse Effect Global Climate Change Organization




Solved 1 Greenhouse Gases And Temperature Simple Model In Chegg Com




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki



1
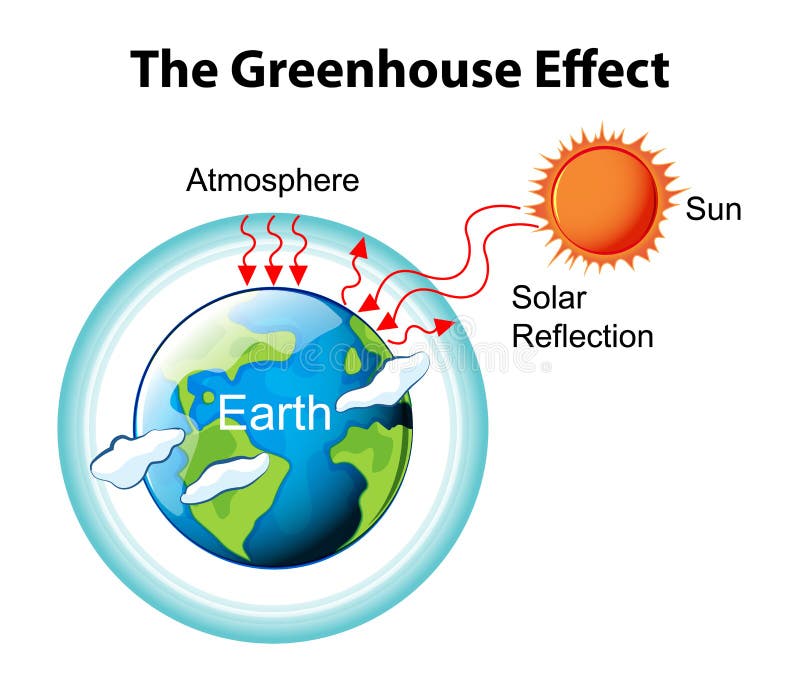



The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Environmental Poster




Greenhouse Effect Model Science Exhibition Project Diy School Fair Project Youtube




Ecology Lab The Greenhouse Effect Modeling And Graphing Efecto Invernadero Ensenanza Biologia Laboratorios De Ciencias




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Lesson For Kids Study Com




Simple Earth Climate Model Single Layer Imperfect Greenhouse Atmosphere
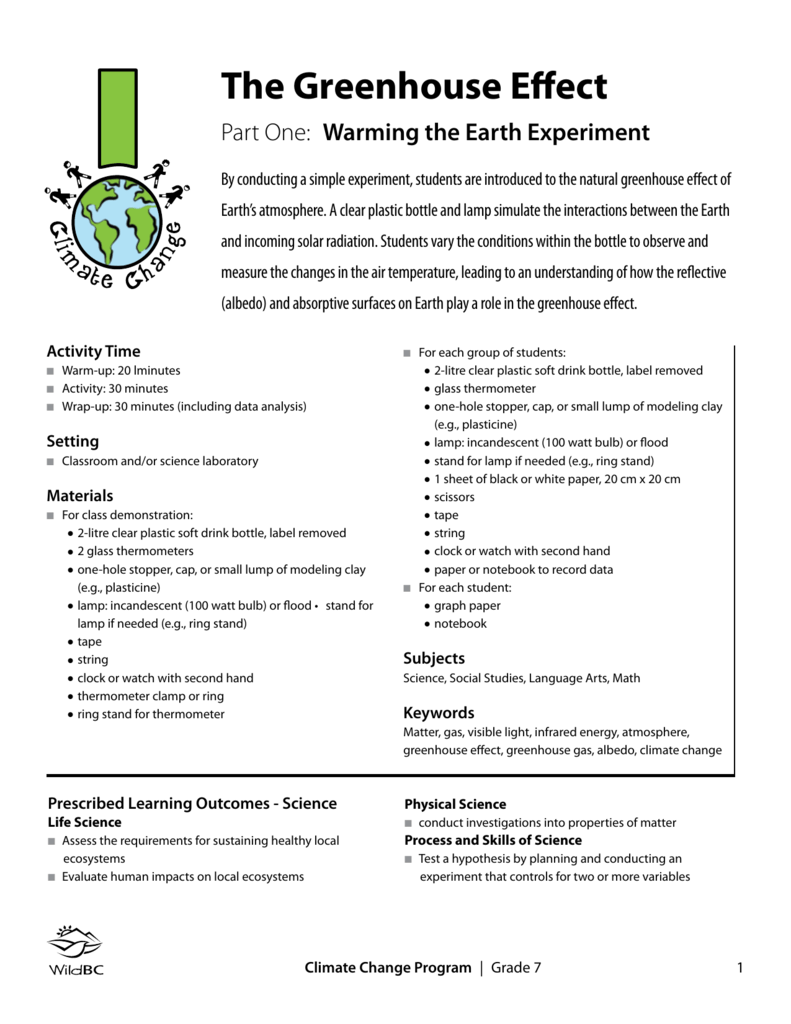



The Greenhouse Effect
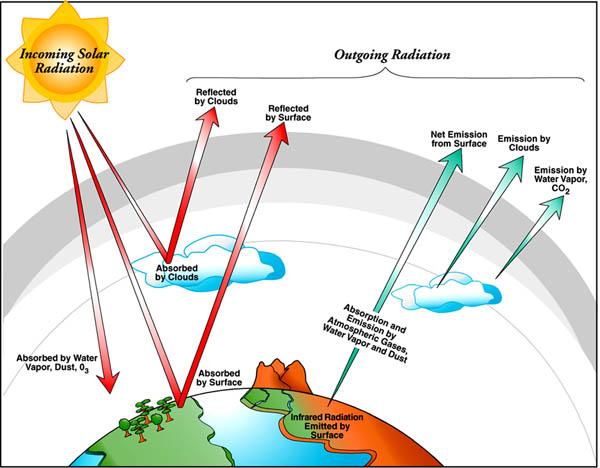



Lab 2 Climate And Earth S Energy Balance




Rrb Ntpc Exam 16 Science Made Simple Inf 8 Green House Effect Ibps Sbi Ssc Rrb Rbi Lic Railways



Future Projection Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Due To Permafrost Degradation Using A Simple Numerical Scheme With A Global Land Surface Model Progress In Earth And Planetary Science Full Text




Climate Change Science And Impacts Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems



Ppt Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect



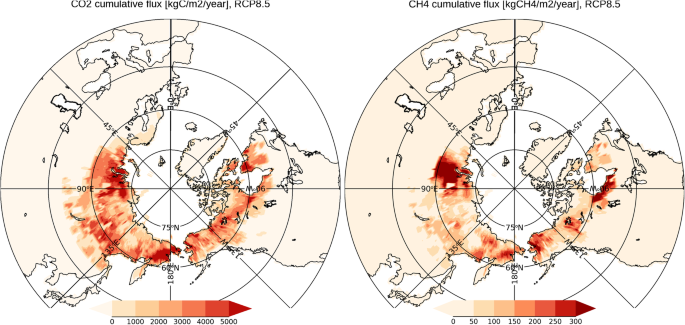
Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
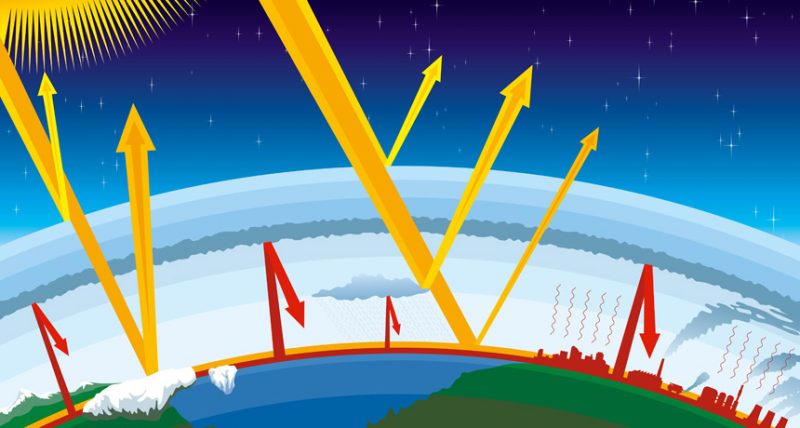




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




Simple Illustration Of Greenhouse Gas Effect Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock
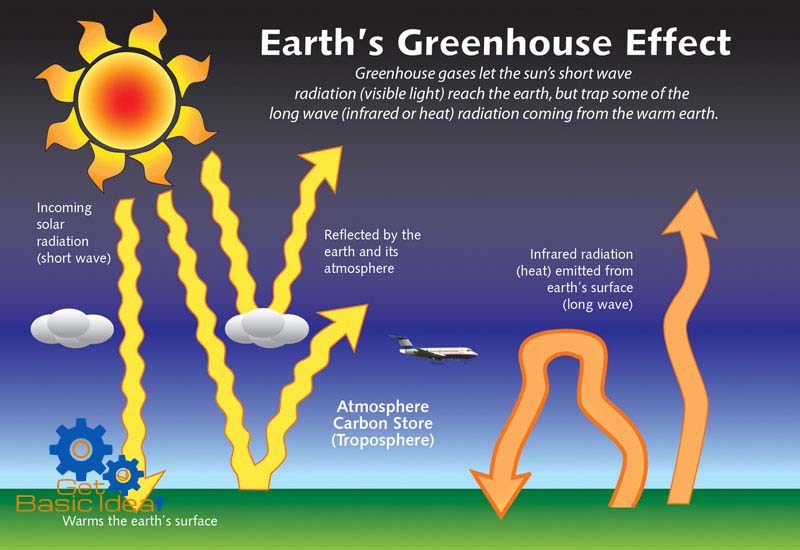



Greenhouse Effect Archives Get Basic Idea




File Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Wikimedia Commons



Simple Time Dependent Model Of The Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Roy Spencer Phd




What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today




Climate Change Science Anyone Can Play With Simple Climate




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Kidminds




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Global Warming How To Reduce Carbon Footprint Global Dimming Gcse Chemistry Revision Notes Igcse Revising Ks4 Science




Develop A Greenhouse Effect Model With 2 Atmospheric Chegg Com




The Greenhouse Effect Experiment And Lesson For Kids




The Greenhouse Effect Eere Energy Gov 08 Download Scientific Diagram
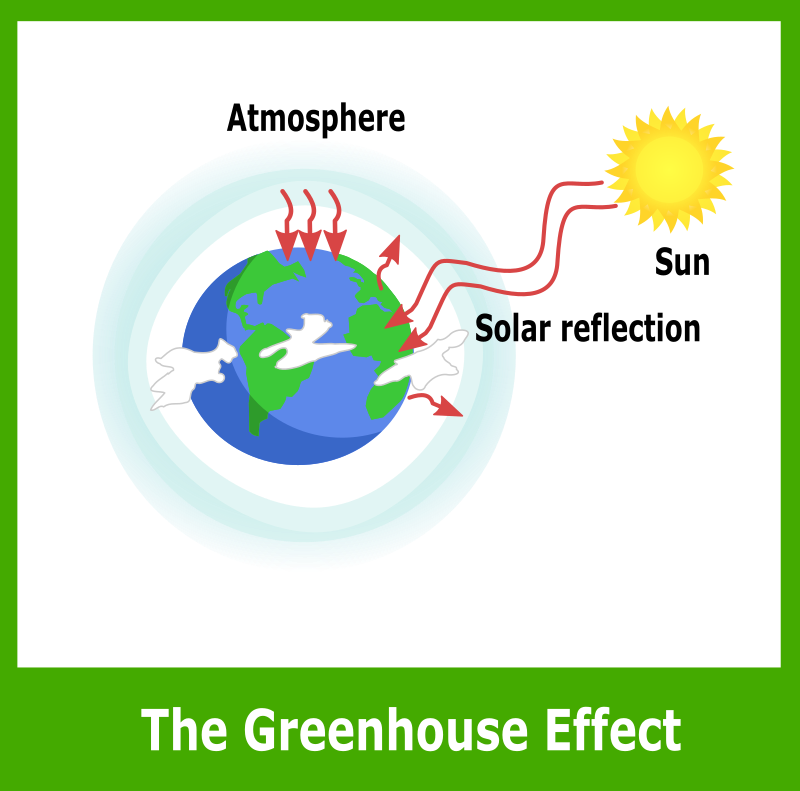



Simple Greenhouse Effect Diagram Openclipart
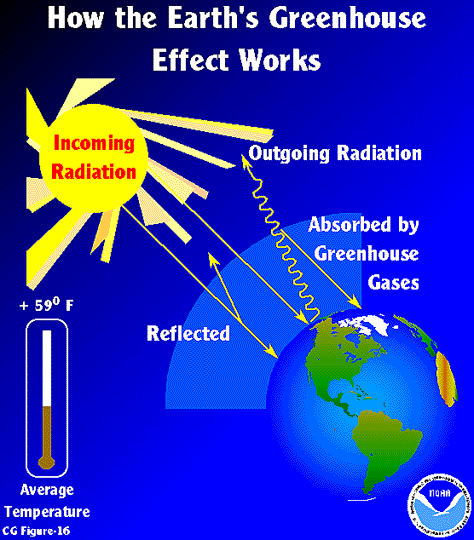



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education



Greenhouse Effect Icon Simple Element From Global Vector Image




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters



The Greenhouse Effect




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




2 A Simple Model Of The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Idealized Greenhouse Model Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
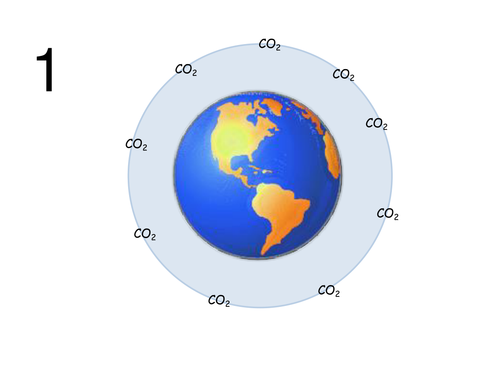



Super Simple Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Teaching Resources




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society



1
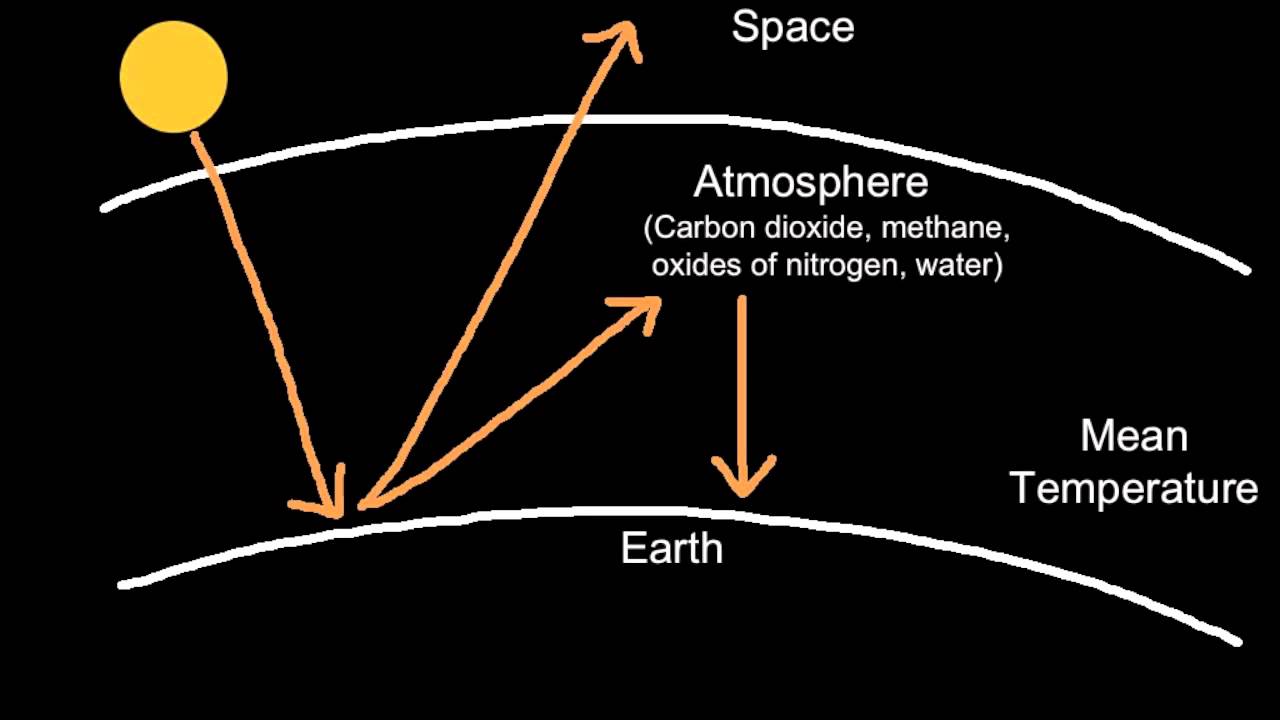



5 2 3 Explain The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Youtube
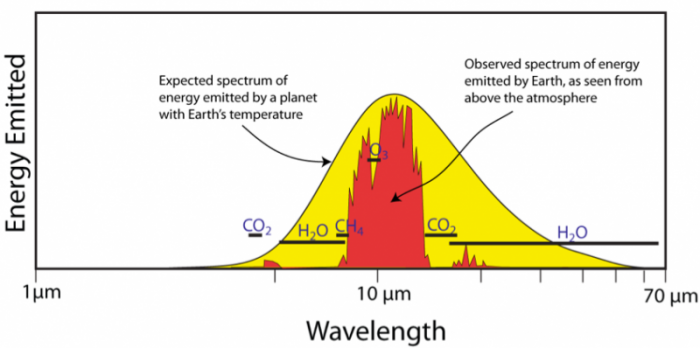



The Greenhouse Effect And The Global Energy Budget Earth 103 Earth In The Future
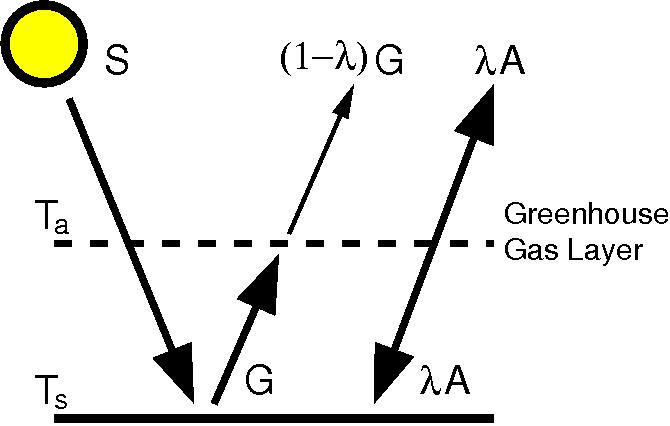



Realclimate Learning From A Simple Model
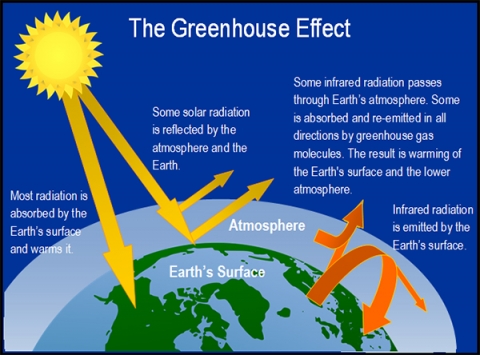



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Let S Talk Science




Modeling The Greenhouse Effect Experiment Ngss Aligned Stem Tpt




Graphic The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




Greenhouse Effect Model School Project For Students Exhibition Models The4pillars Youtube
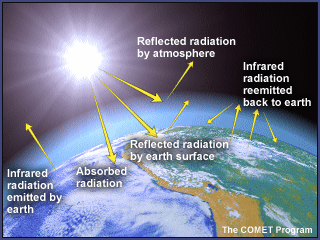



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
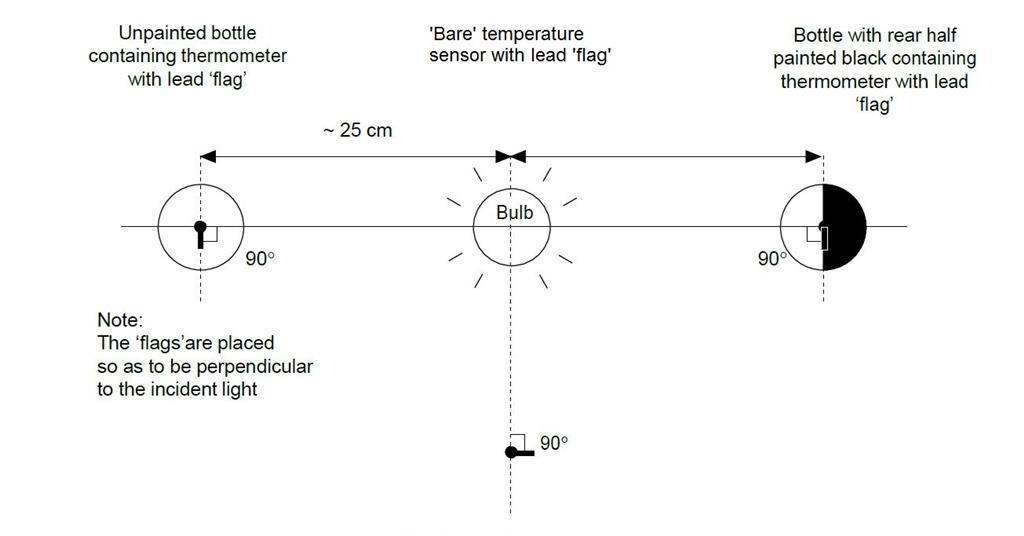



Modelling The Greenhouse Effect Experiment Rsc Education




Greenhouse Effect Department Of Agriculture Water And The Environment




Global Warming Simple Physics In A Compex System
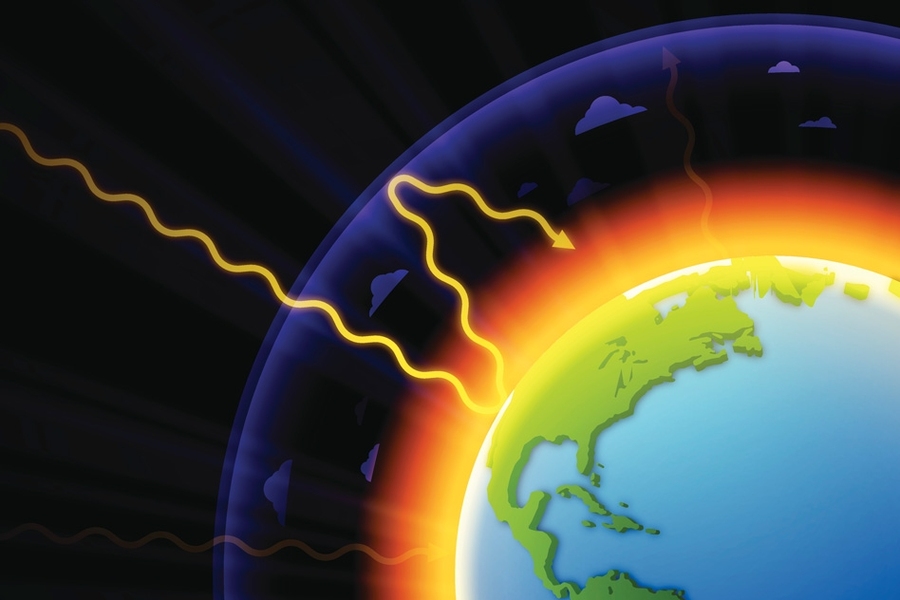




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology




Simple Greenhouse Model




Global Warming Computer Models Are Largely Right Refuting Climate Denial Talking Point The Washington Post




What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide




13 The Carbon Cycle Ideas Carbon Cycle Carbon Atmospheric Gases



Global Warming Greenhouse Gas Models For Kids




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿